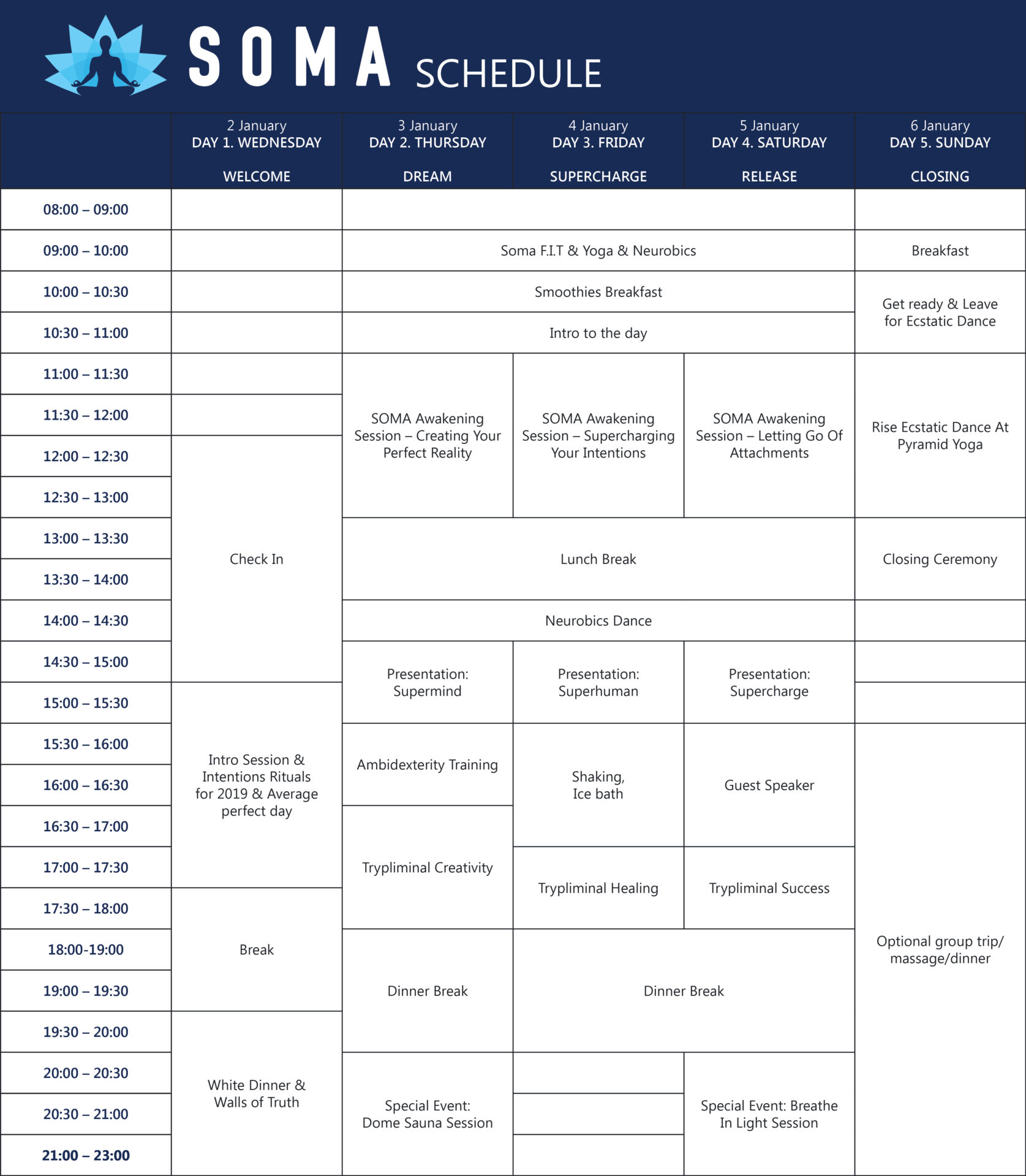
The Science
Of SOMA Breath
SOMA Breath is a leading breathwork school and research institution that has garnered global attention from some of the biggest names in the wellness industry, including Cambridge University.
Uncover the Scientific Foundations of SOMA Breathwork and its Profound Influence on the Well-Being of Participants.
Results of The Cambridge University Study on SOMA Breath Techniques

A comprehensive study conducted by researchers at the University of Cambridge has shed light on the impact of SOMA Breath on brainwave activity and mental health/wellness.
Notably, the breathwork meditation techniques associated with SOMA Breath induced significant alterations in brainwave patterns as reported by the Cambridge Study. Surprisingly these changes are remarkably similar to those observed in mental health treatments involving traditional psychedelics.
The participants of the SOMA breathwork meditation study reported enhanced feelings of unity and spirituality, exceeding those observed in prior Psilocybin (Magic Mushrooms) and MDMA studies.
“We chose to collaborate with Soma due to its very clear and systematic approach, and the effectiveness of the method as per clear reports from those participating and the researchers coordinating the study.”

Dr Tristan Bekinschtein Cambridge University
The study also found that SOMA Breath meditation positively affects mood, reducing negative emotions like tension and confusion while enhancing positive states such as happiness and calmness.
With the results of this study suggesting that SOMA Breathwork could mimic traditional psychedelics' states, they offer potential hypnotic and mood-enhancing benefits, helpful in processing past traumas and instilling new subconscious beliefs and behaviours. This research builds on Dr. Jeff Tarrant's earlier study at the Neuro Meditation Institute, which demonstrated SOMA Breath's efficacy also in alleviating conditions of anxiety and depression.
This research collaboration with Cambridge University is a significant milestone for the global breathwork community. Dr. Tristan Bekinschtein of Cambridge explained that they chose SOMA Breath due to SOMA Breath's systematic approach and effectiveness, as reported by participants and researchers. The current ongoing research at Cambridge, involving comprehensive case studies and clinical trials, aims to further deepen our understanding of SOMA Breath's role in treating mental health issues, potentially offering new, non-pharmacological treatment options.

The Science Behind Breathwork
Breathwork, a practice deeply rooted in ancient traditions, has garnered significant attention in the modern wellness landscape for its profound impact on mental and physical health. At its core, breathwork involves consciously altering breathing patterns to influence the body's physiological and psychological state, resulting in enhanced well-being and stress management.
The science behind breathwork centers on its ability to regulate the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary bodily functions like heart rate and digestion. By modulating breathing, one can shift from the sympathetic nervous system (SNS), often associated with the 'fight or flight' response, to the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS), which promotes 'rest and digest' activities. This transition is crucial for stress reduction, as it lowers cortisol levels and reduces blood pressure, fostering a state of calm and relaxation.
Moreover, breathwork influences the brain's chemistry. Controlled breathing can increase the level of oxygen in the brain, enhancing cognitive function and emotional regulation. It stimulates the release of endorphins, the body's natural painkillers, leading to improved mood and reduced anxiety. Additionally, practices like deep diaphragmatic breathing enhance lung function and oxygenation of the body, offering physical health benefits.
Research in psychophysiology also underscores the benefits of breathwork in mental health. Techniques like pranayama, a key component in yoga, have been shown to improve symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). By fostering mindfulness and a heightened state of awareness, breathwork aids in emotional processing and resilience.
How SOMA Breath Delivers Its Groundbreaking Benefits

The SOMA Awakening Ceremony is a higher yoga ritual designed to clear negative imprints and help you break free from the past, so you can be more present, in the flow, liberated, and empowered to be the sole creator of your reality.

Rhythmic breathing hyper-oxygenates your body, bringing in more oxygen and blowing out more carbon dioxide than normal. This alters the pH of your bloodstream and also creates a strong electromagnetic field and current to flow through your body. This increases your Level Of Vibrational Energy (L.O.V.E.). With a higher vibrational state, negative emotions and trauma can be cleansed from the mind and body, and your ability to manifest becomes totally effortless. read more

The diaphragmatic breathing technique we teach stimulates the largest lymphatic organ in your body, creating a powerful cleansing effect and strengthening your immune system.

We employ extended exhalation and vocal toning techniques to tap into the power of the vagus nerve to switch off stress and connect with your subconscious mind.
Life is just a series of inhales and exhales; when you pause your breath, you press pause on life.
Your quality of thought is also linked to breath: erratic breathing leads to erratic thinking, while smooth consistent breathing leads to smooth, coherent thought.

The breath retention components of SOMA Breath are totally safe. They allow you a few minutes to totally slow down and pause your life to be fully in the present moment. You enter a profound meditative state and connect to yourself on a personal level.

Using the power of affirmations, guided mental imagery techniques, and self-hypnosis, you can reprogram your subconscious operating system and influence your autonomic nervous system.

The activation of Yogic energetic locks throughout the SOMA Awakening Ceremony creates sexual energy, which is the source of creativity and imagination. You experience states of ecstatic bliss and many different states of consciousness.

Powerful emotional releases can occur during SOMA Breath sessions, and negative imprints from the past can be cleared. “Divine downloads” or moments of deep insight and inspiration make the SOMA Breath experience truly unforgettable.
Reviews from Respected Industry Leaders
“The breathwork modality I do is Soma Breath®. Its really cool as they incorporate incredible music into it. It's the best alternative to the impact you can get from plant medicines today, but safer and more effective.”

Vishen Lakhiani CEO of Mindvalley
“We chose to collaborate with Soma due to its very clear and systematic approach, and the effectiveness of the method as per clear reports from those participating and the researchers coordinating the study.”

Dr Tristan Bekinschtein Cambridge University
“Soma Breath® is the gold standard for breathwork, I recommend this to all my RTT therapists”

Marisa Peer Therapist
“I can personally say that regularly practicing SOMA breathing techniques has dramatically increased my physical health, mental, and emotional wellbeing, spiritual connection, and because I’ve been able to incorporate my boys and Jessa into many of my SOMA sessions, even my relationship with my family.”

Ben Greenfield Health Consultant and New York Times Bestselling Author
What Is The Actual Process of Respiration?
Respiration involves the inhalation of a mixture of oxygen (O2) and other molecular gases and the exhalation of a mixture of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and other gaseous molecules. Breathing in increases your heart rate slightly while breathing out lowers it slightly. Interestingly enough, the process of respiration also has implications for the body’s metabolism.
As you breathe in, oxygen (O₂) binds with red blood cells present in the capillaries (small blood vessels) of the lungs. The oxygenated blood then travels through the bloodstream to supply tissues and cells with oxygen. Once the oxygenated blood reaches the mitochondria inside the body cells, the oxygen combines with glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), more simply known as energy. This reaction powers the body system and provides the energy needed for daily function. By-products like water vapour (H₂O) and carbon dioxide, which are exhaled, are also produced from this reaction.
How Does The Circulatory System Play A Role in Respiration?
The circulatory system provides a means for oxygen delivery to mitochondria within cells to continue producing energy to sustain the body. It also allows the means of eliminating cellular waste from the body, such as carbon dioxide. The blood circulation through the body is powered by the pumping action of the heart, which pulses blood through the veins and arteries of the body.
Why Is Breathwork Important?
The Importance of Balancing the Breath
The circulatory system provides a means for oxygen delivery to mitochondria within cells to continue producing energy to sustain the body. It also allows the means of eliminating cellular waste from the body, such as carbon dioxide. The blood circulation through the body is powered by the pumping action of the heart, which pulses blood through the veins and arteries of the body.
Your Breath and the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system, comprising the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, autonomously regulates functions like heart rate, pupil dilation and saliva production. Our breathing influences these systems: inhaling activates the sympathetic system, energizing the body, while exhaling stimulates the parasympathetic system, aiding relaxation.
The continuous process of inhalation and exhalation keeps these two systems balanced. The faster you breathe, the faster you take in oxygen and remove CO2, thereby stimulating sympathetic nerves and invigorating your body.
Conversely, slow, deep breathing with prolonged exhalation leads to increased CO2 and decreased O2, causing vasodilation— lowered blood pressure & increase in blood flow. Thus, breathing pace controls these bodily processes and energy utilization efficiency.

How Inefficient Breathing Affects Your Body
Breathing is an unconscious action that is not taught nor trained when we come into this world. Stress, illnesses and various daily activities can cause us to unknowingly adopt variable, ineffective breathing patterns which do not support our health and put us in a state of oxidative stress. At times, you may even unconsciously pause your breathing. The way we breathe affects many bodily processes and even influences the rhythm at which our heartbeats.
Incoherent breathing activates the sympathetic nervous system and can cause an inefficiency in our cellular machinery and bodily function. Breathing in too much oxygen at a time can cause oxidative stress, which can be thought of as the rusting of the arteries and veins. Just like oxygen reacts with metal, causing corrosion over time, so too does excessive oxidation of our cells. Excessive oxygen in the red blood cells leads to inflammation, plaque and corrosion, which complicates the natural order of respiration. Oxidative stress can stem from excessive exercise and doing too many strenuous physical activities that cause you to breathe erratically as well.
Additionally, oxidative stress increases the amount of free radicals in your system. Free radicals attack proteins and DNA, causing tissue damage, inflammation and death of cells. Oxidative stress has also been implicated as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases, cancer and autoimmune medical conditions. Some studies also show that inefficient respiration also precedes mental conditions such as depression, low mood and lack of motivation.
This process is synonymous with the oxidation of some metals when exposed to air, which causes rusting. In the same way, the human body can stop working efficiently, leading to inflammation and cell damage. This is why the conscious control of the amount of oxygen in the bloodstream through inhalation and exhalation can benefit the body system.
The Balance of Oxygen & Carbon Dioxide
The Bohr effect is known as the lowering of blood pH caused by high CO2 concentration. This lowering of the pH of the blood enables the hemoglobin molecule to release the oxygen attached to it. This effect is what allows the mitochondria to receive the oxygen needed to create ATP energy.
In contrast, when your body is under oxidative stress due to hyperventilation or excessive breathing, there is too little CO2 in the cells to facilitate the release of oxygen from the hemoglobin. This, in turn, results in low production of ATP energy, which helps the body system function normally. Therefore, the brief presence of CO2 in the body before exhalation serves an important purpose.
SOMA Breath is aimed at helping you by giving you the tools and techniques to breathe more efficiently and with more awareness. The power of learning to control and balance your breath for consistent production of ATP energy will allow you to feel more vibrant and more productive every day and help to ward off disease caused by oxidative stress. Experience the energizing and relaxing effects of SOMA Breath and develop resilience from day-to-day stressors for better overall health, wellness and longevity. Unlock your body’s natural healing potential with SOMA Breath.
In conclusion, the science of breathwork lies at the intersection of physiology and mindfulness. Its ability to regulate the nervous system, alter brain chemistry, and enhance emotional well-being makes it a powerful tool in the pursuit of holistic health. As more scientific studies delve into its benefits, breathwork continues to emerge as a vital component of modern wellness practices. Respiration is a crucial, complex process that integrates with the body's circulatory and nervous systems. It is not just about exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide but also maintaining their balance for cellular health. Proper breathing ensures effective oxygen delivery for energy production and prevents oxidative stress, essential for avoiding cellular damage. Efficient breathing is vital for overall health, and techniques like SOMA Breath can enhance this, promoting physical and mental well-being.
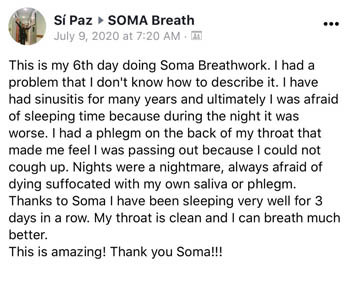
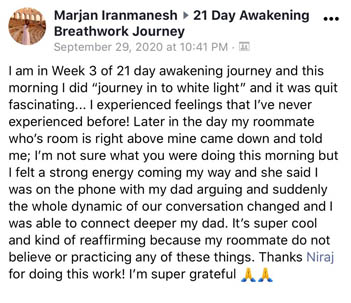
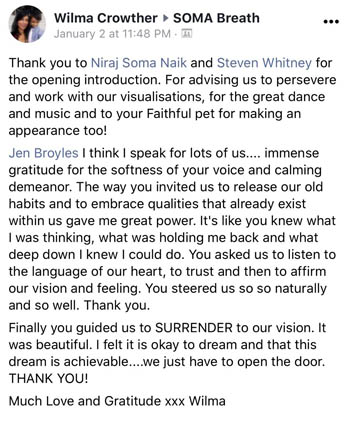
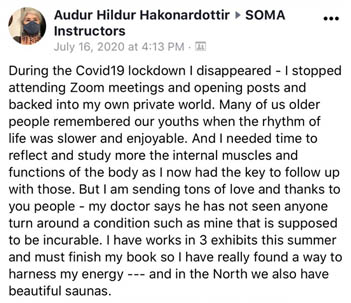
Participant Reviews
Take a look at what our attendees have to say about their SOMA Breath Experience








The Benefits of SOMA Breath
Enhanced oxygen utilization efficiency
Improved carbon dioxide tolerance
Strengthened mind-body connection
Boosted cardiovascular health, including increased stamina, endurance, and overall fitness
Reduction in inflammation
Balanced nervous system
Deep meditative states
Heightened mental and physical resilience
Facilitation of mind reprogramming and self-hypnosis for self-improvement
A calmer, clearer mind leading to better judgment and decision-making
Effective stress management
Awakening to one's soul's purpose and authentic self
Increased confidence and self-esteem
Facilitated emotional processing and release

SOMA Breath Instructor Training Certification Program
Become a certified breathwork instructor with world-class breathwork training. The advanced Breathwork Teacher Training Certification program is a comprehensive and rigorous journey designed for aspiring instructors. This program is a gateway to obtaining the prestigious SOMA Breath instructor training certification, recognized globally for its excellence. Participants undergo intensive training and thorough testing, ensuring they are well-equipped with the knowledge and skills required to conduct SOMA Breathwork ceremonies.
Limited Time Offer
FREE SOMA Breath® Masterclass
Join the FREE SOMA Breath® Masterclass and elevate every aspect of your life, from immunity and self-healing to happiness and manifestations. Discover the transformative power of ancient breathwork, innovative music, and advanced visualizations in a dynamic 40-minute online session.
You can participate from anywhere for FREE!
Join the SOMA Breath Community
Join our vibrant SOMA Breath Facebook Community! Get the latest updates, tips, and connect with fellow SOMA enthusiasts.